Beginners Guide to Argo CD
Learn, Implement and Share about Argo CD after this 15 minutes read.
Before getting hands-on with Argo CD, we are going to discuss What Argo CD is, How it works, and What prerequisites you need.
What is Argo CD ?
Argo CD is a Kubernetes-native continuous deployment (CD) tool. Unlike external CD tools that only enable push-based deployments, Argo CD can pull updated code from Git repositories and deploy it directly to Kubernetes resources. It enables developers to manage both infrastructure configuration and application updates in one system.
Argo CD offers the following key features and capabilities:
- Manual or automatic deployment of applications to a Kubernetes cluster.
- Automatic synchronization of application state to the current version of declarative configuration.
- Web user interface and command-line interface (CLI).
- Ability to visualize deployment issues, detect and remediate configuration drift.
- Role-based access control (RBAC) enables multi-cluster management.
- Single sign-on (SSO) with providers such as GitLab, GitHub, Microsoft, OAuth2, OIDC, LinkedIn, LDAP, and SAML 2.0
- Support for webhooks triggering actions in GitLab, GitHub, and BitBucket.
With fewer words, we can say Argo CD is a GitOps agent that maintains the desired state of a cluster.
Let me explain, suppose there is an application you built, and you want it to run on a cluster with 3 Pods and 2 Services for external IPs. This is the desired state you want and whenever changes happen in your application's repository or if at any moment, your desired state is not present in that cluster, you need to check and do some changes to the cluster to get your desired state running, this is a manual process. And here comes Argo CD to automate the whole process with GitOps principles where we use Git as the data provider of that application and cluster state.
How does Argo CD work ?
As we know, Agro CD ensures that the cluster is running in the desired state at all times. Then a question rises how does it work then ?
It's simple, there will be two repositories, one holding the application you build and the other one holding the declaratively written desired state of the cluster. Argo CD as a Kubernetes controller can be installed in the same cluster where our application is or it can also perform its tasks from an external cluster. It checks whether the current state of the running cluster matches with the written desired state, if it doesn't then Argo CD will try to make the desired state and synchronize everything.
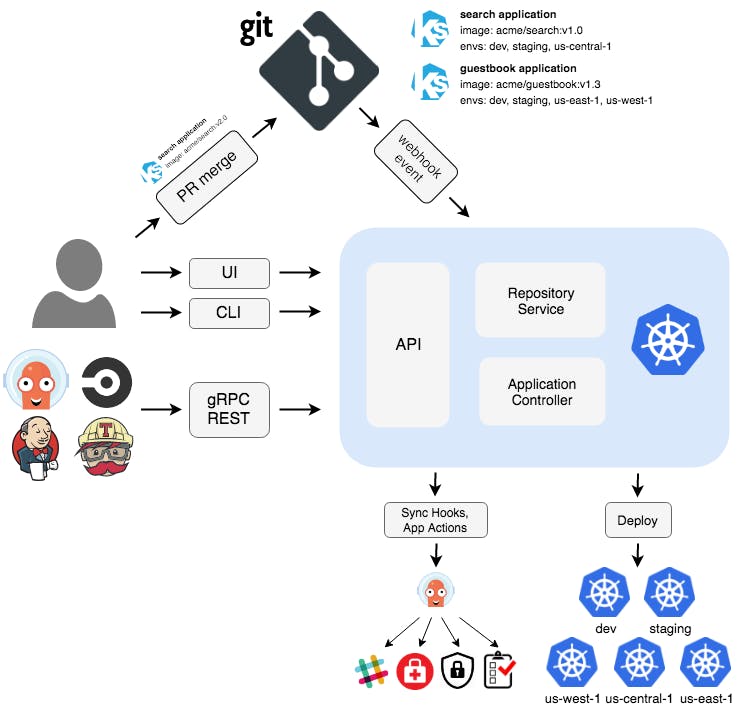 For a better understanding of its architecture, visit Argo CD Documentation.
For a better understanding of its architecture, visit Argo CD Documentation.
When Argo CD checks that the live and desired states are different, it shows OutOfSync in its UI, yes it does have a UI as well as CLI, whatever you wish to use. And if it matches then Everything is fine, its status return Synced.
It supports plain Kubernetes manifests, Helm charts, Kustomize definitions, and other templating mechanisms.
By default, Argo CD looks for any changes in our repository every 3 minutes. If there are any changes in our repositories, Argo CD will update our cluster with the new changes we desired. But if we want Argo CD to look for changes every second, we can do that too and if you don't like this mechanism of checking for changes then you can use webhooks too where Argo CD receives notifications from your git provider and when it receives a notification from your application's repo, it will look for changes.
Check core concepts of Argo CD from this link core-concepts.
Prerequisites
- Basic knowledge of Git, K8s, and Networking.
- Tools - kubectl, minikube (optional), docker (optional).
Implementation of Argo CD
- Q. What will we be doing today ?
- A. Deploy a Docker application in a Kubernetes cluster which is declaratively described in plain Kubernetes manifest files in a Github Repo.
In this article, I have used this repo Webserver-CI-CD-Golang
For this demo, I am using Minikube for a local cluster. Or you can create your Argo CD setup in Codefresh Course.
- Installation of Argo CD
Argo CD can be used to deploy and manage other applications, do not forget that it is also an application by itself. There are many ways to install it on a Kubernetes cluster.
For the experiment, You can deploy Argo CD by directly using the manifest,
kubectl create namespace argocd
kubectl apply -n argocd -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/argoproj/argo-cd/stable/manifests/install.yaml
For a production setup, we suggest you use Autopilot, a companion project that not only installs Argo CD but commits all configuration to git so Argo CD can manage itself using GitOps.
For more traditional installation options, the manifests directory offers different modes of installation with or without High Availability. The installs marked as “namespace” allow you to install Argo CD on a single namespace without cluster-wide privileges. This is best when you want to install Argo CD on one cluster but have it manage other external clusters.
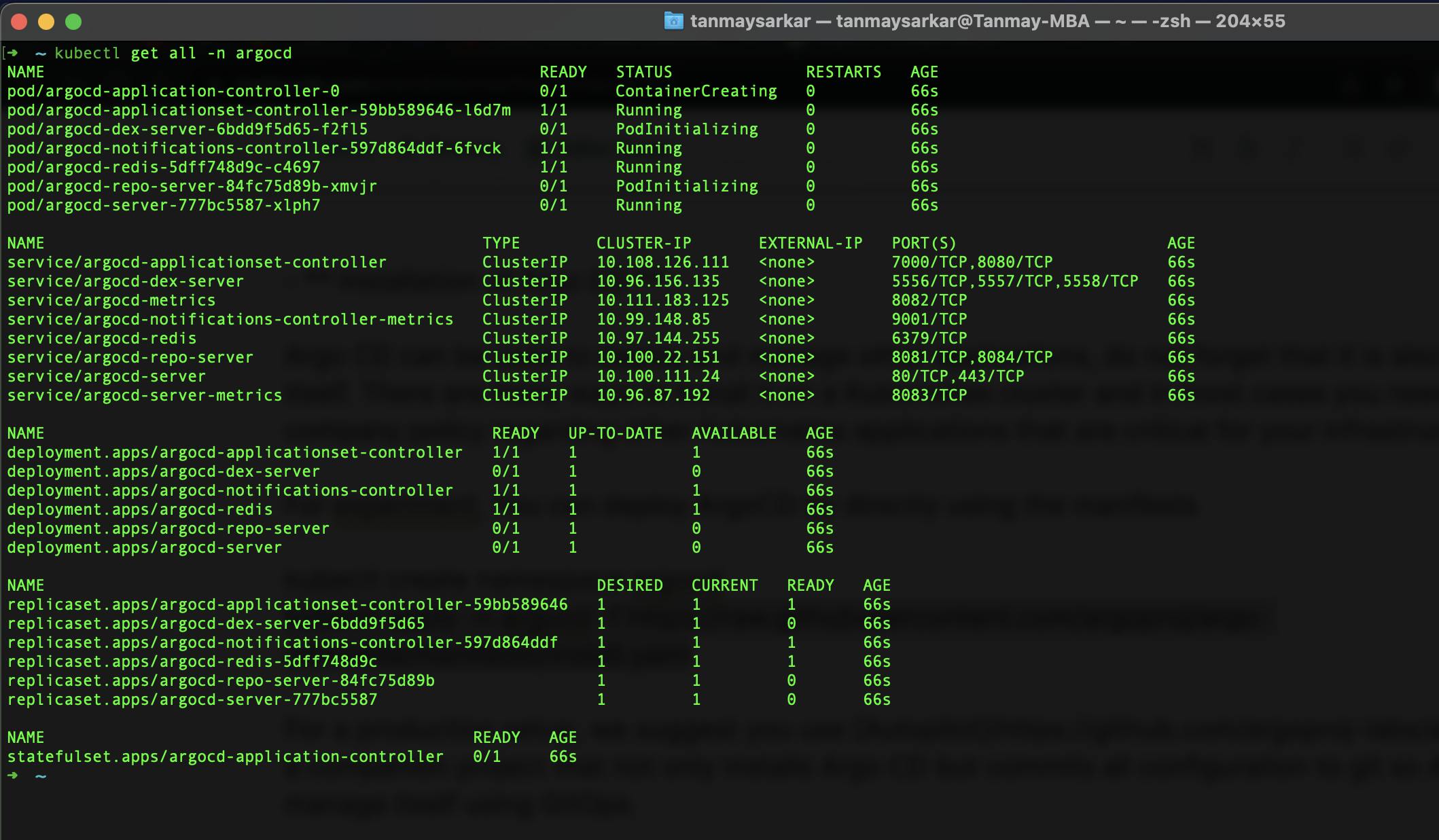
See all resources created by Argo CD -
kubectl get all -n argocd
- Expose Argo CD UI
By default, Argo CD is only accessible from within the cluster. To expose the UI you can utilize any of the standard Kubernetes networking mechanisms such as -
- Ingress (recommended for production)
- Load balancer (affects cloud cost)
- NodePort (simple but not very flexible)
Once the external URL is ready, you need to decide how users will access the Argo CD UI. There are mainly two approaches:
- Use a small number of local users. Authentication is handled by Argo CD itself. Best for very small companies (e.g. 2-5 people).
- Use an SSO provider. Authentication is handled by the provider. Ideal for companies and large organizations.
To expose using Ingress,
kubectl port-forward svc/argocd-server -n argocd 8085:443
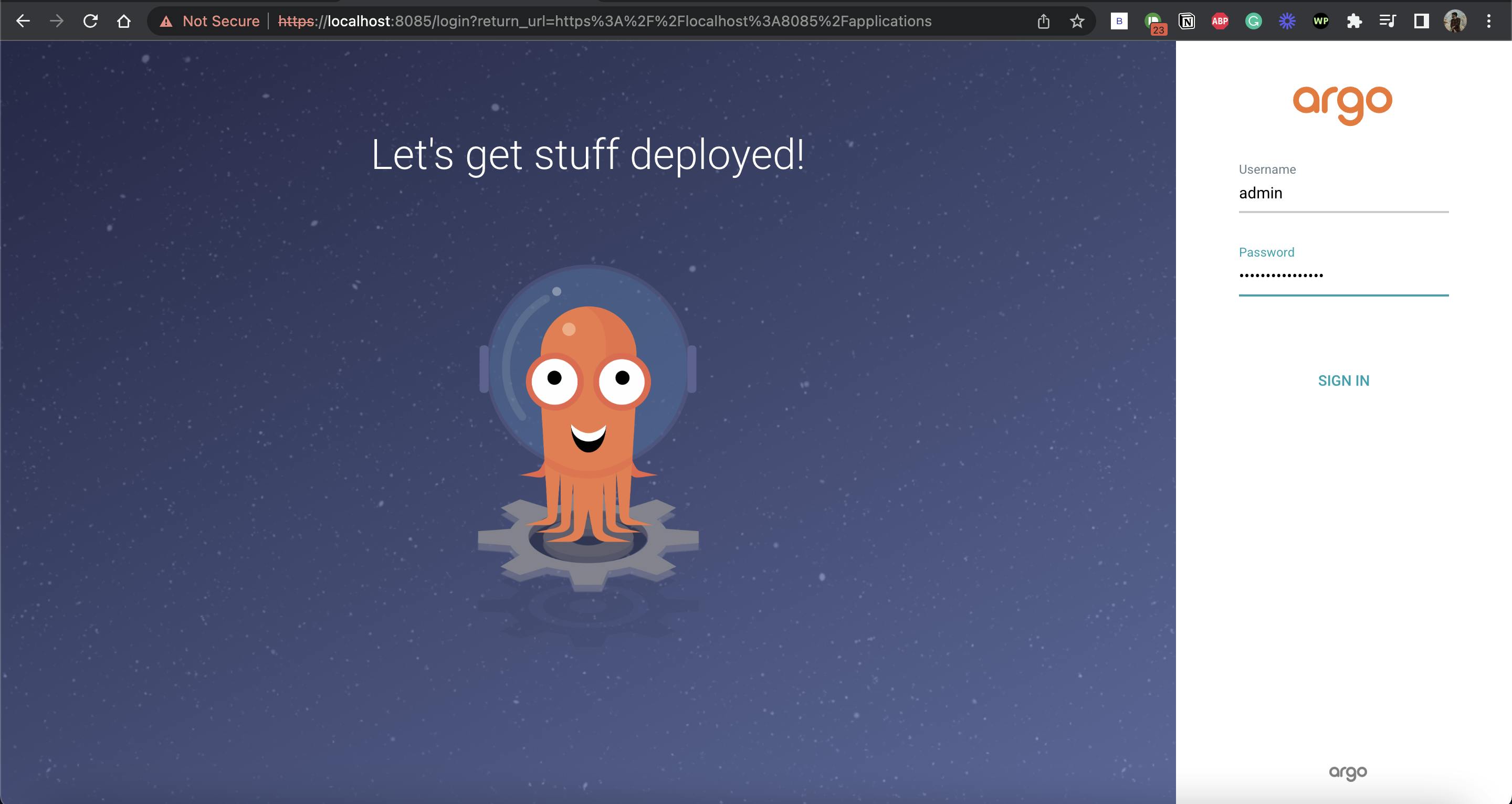
Now, visit localhost:8085 for Argo CD UI.
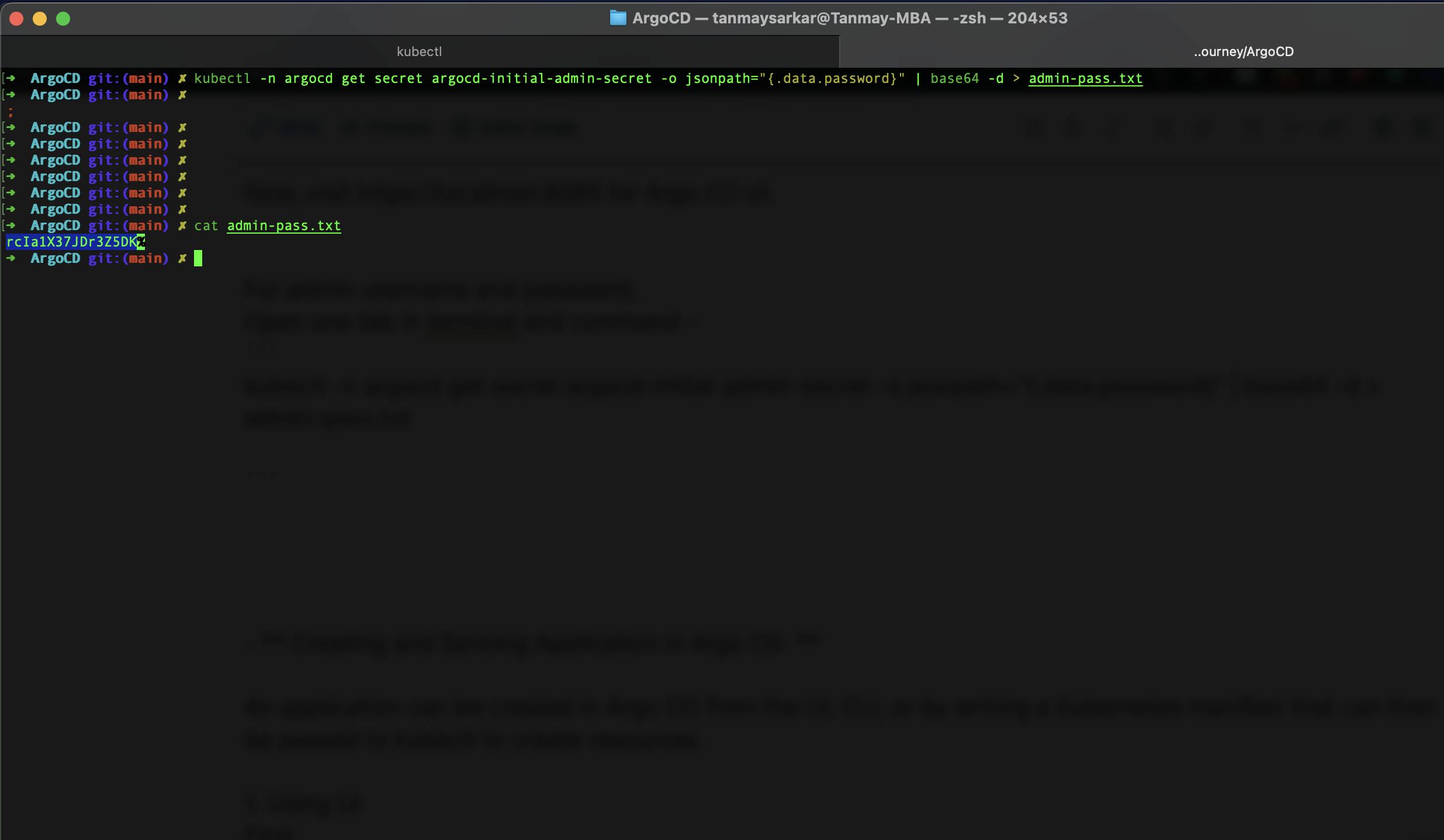
For admin username and password, Open another tab in the terminal and command -
kubectl -n argocd get secret argocd-initial-admin-secret -o jsonpath="{.data.password}" | base64 -d > admin-pass.txt
Now, login to the admin account -
- Creating and Syncing Application in Argo CD
An application can be created in Argo CD from the UI, CLI, or by writing a Kubernetes manifest that can then be passed to kubectl to create resources.
Using UI
1. Click on NEW APP
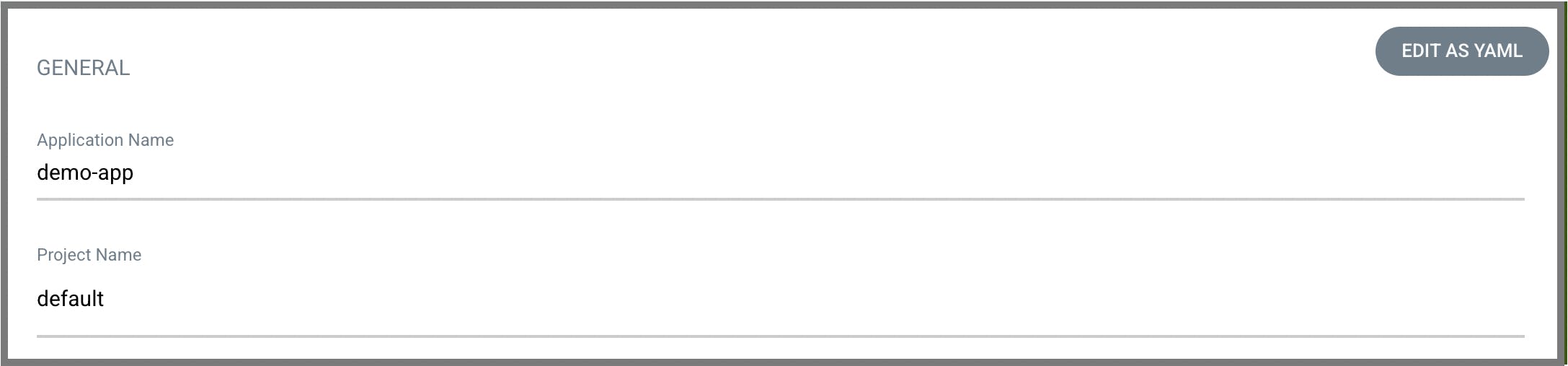
2. Put only necessaries as mentioned below
General
Application Name:
demo-appProject Name:
default
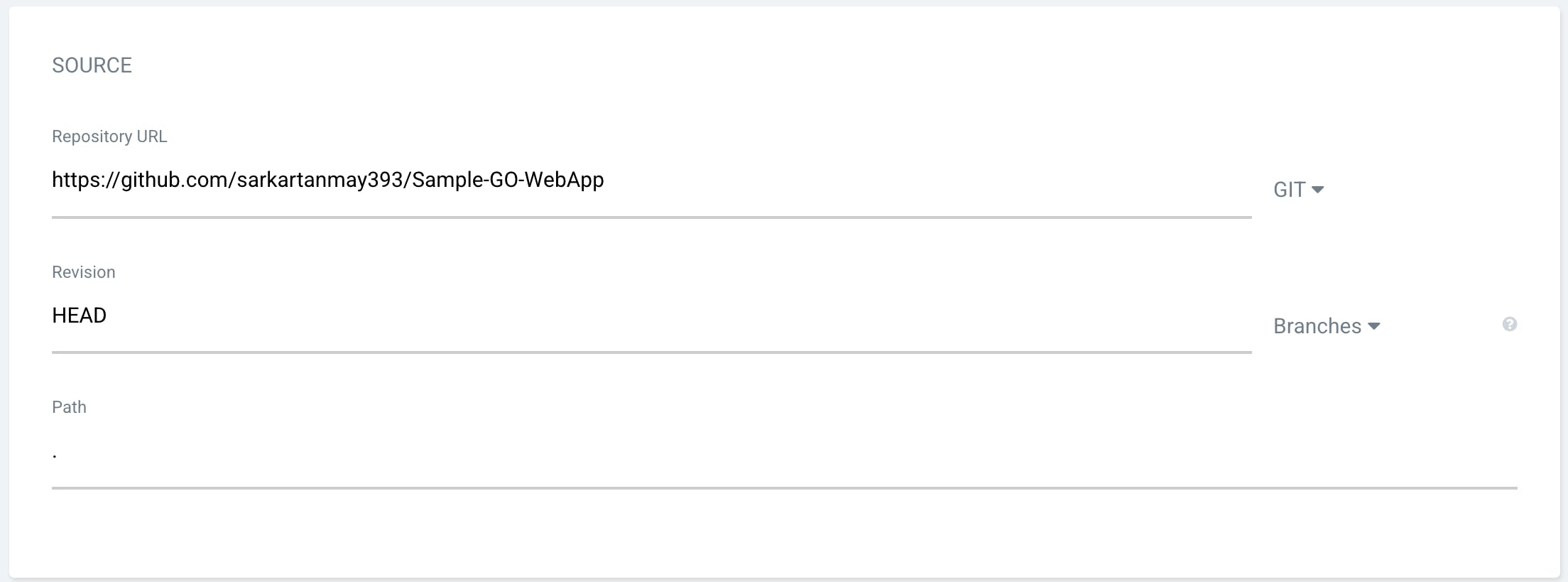
Source
Repository URL:
https://github.com/sarkartanmay393/Sample-GO-WebAppRevision:
HEADPATH:
.
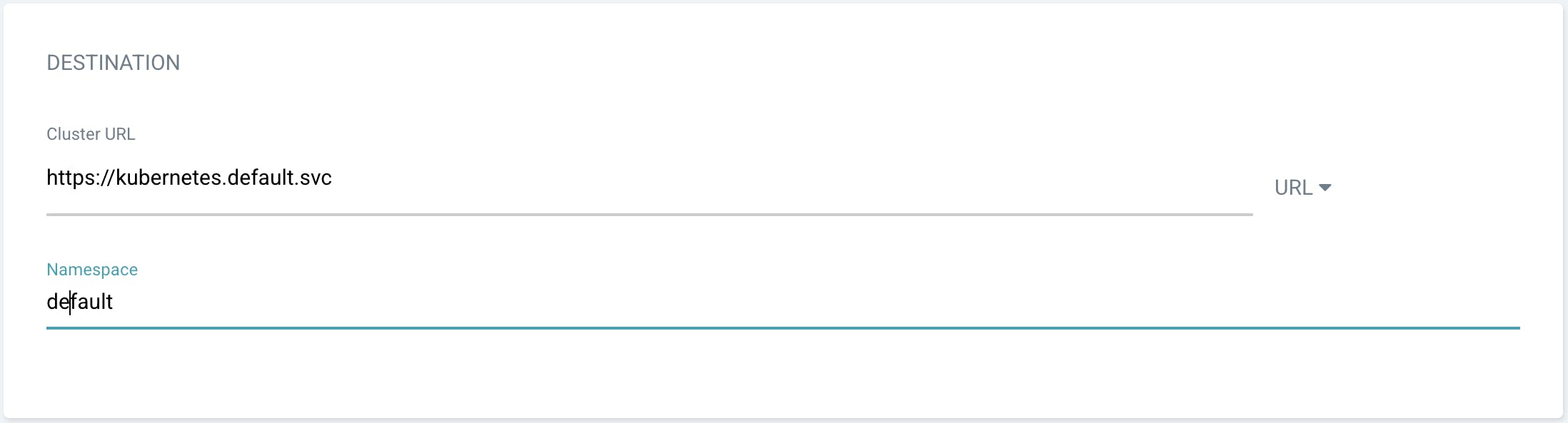
Destination
Cluster URL:
https://kubernetes.default.svcnamespace:
default
YAML File -
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Application
metadata:
name: demo-app
spec:
destination:
name: ''
namespace: default
server: 'https://kubernetes.default.svc'
source:
path: .
repoURL: 'https://github.com/sarkartanmay393/Sample-GO-WebApp'
targetRevision: HEAD
project: default
Check your YAML by hitting EDIT AS YAML and try to understand.
Now, Press on Create and You will see this on screen.
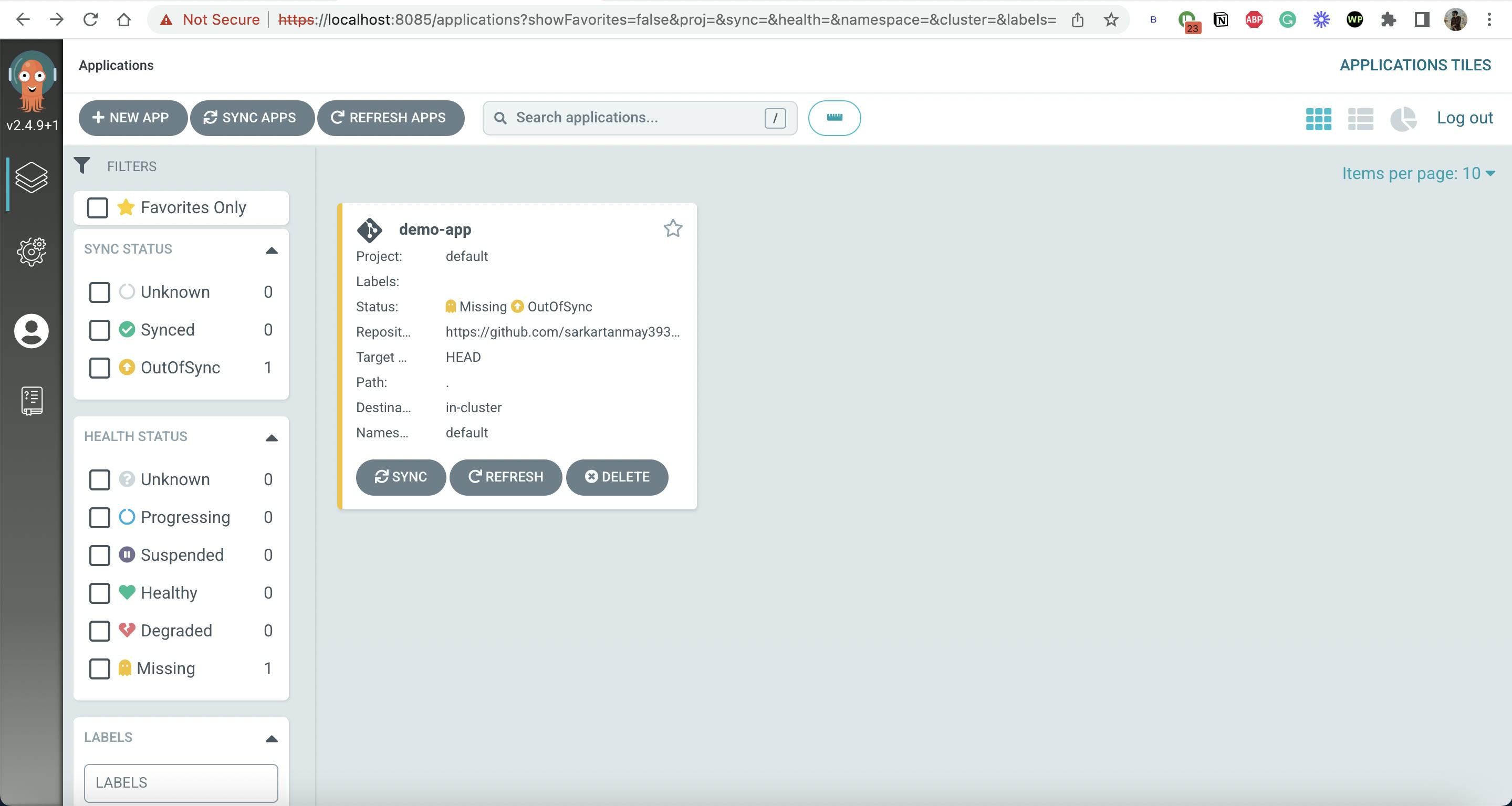
Now, click on SYNC and Proceed without any change.
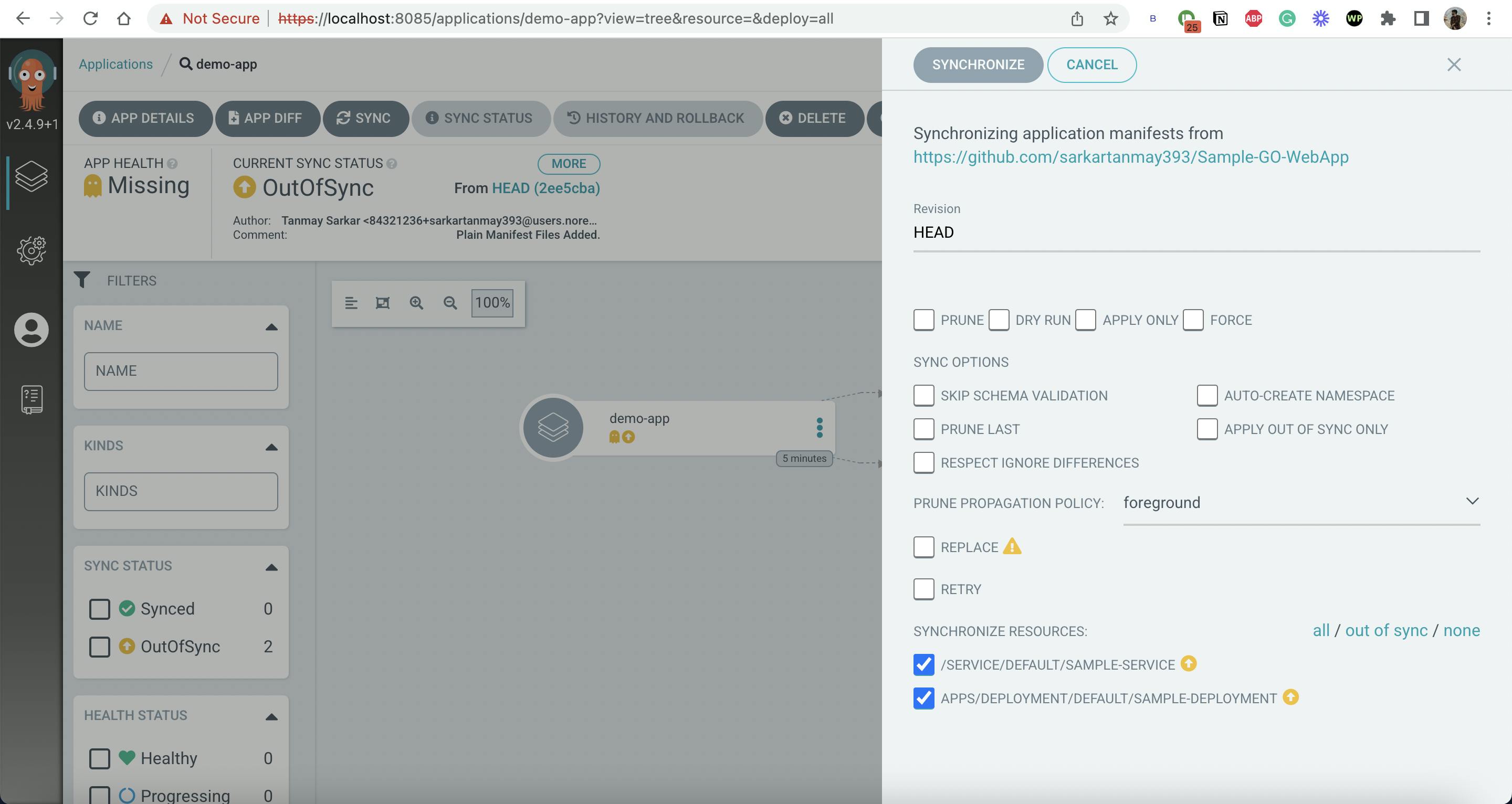
Using CLI
1. Install Argo CD CLI
Run the following command -
For Linux :
curl -sSL -o /usr/local/bin/argocd https://github.com/argoproj/argo-cd/releases/latest/download/argocd-linux-amd64
chmod +x /usr/local/bin/argocd
For Mac :
brew install argocd
I am using this mac command as I am working with a local cluster. Use this reference to install Argo CD CLI.
Argo CD CLI Help Screen -
2. Login Argo CD CLI
Run the command -
argocd login localhost:8085
Then continue with y and,
Username: admin
Password: check your admin-pass.txt
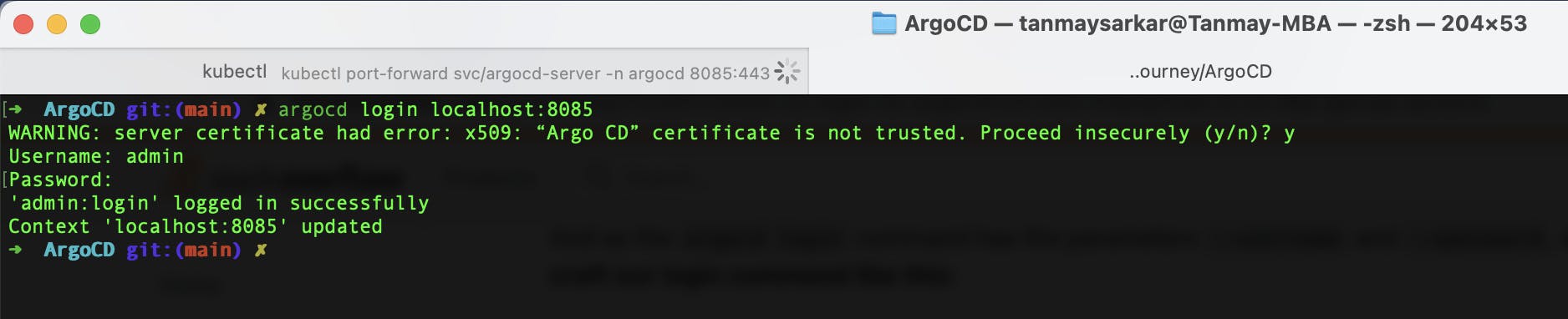
I am login into our localhost server because it is the argocd-server that was port forwarded earlier.
For Further reference, tap here.
3. Create an app in CLI
Run the following command -
argocd app create demo-app --project default --repo https://github.com/sarkartanmay393/Sample-GO-WebApp --path . --dest-namespace default --dest-server https://kubernetes.default.svc
This will be output -
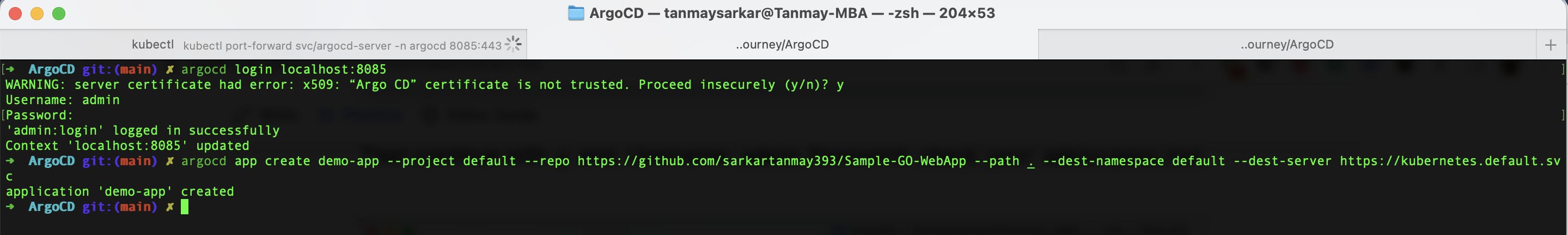
Some other Argo CD commands -
➜ argocd app list #See all apps in Argo cd
NAME CLUSTER NAMESPACE PROJECT STATUS HEALTH SYNCPOLICY CONDITIONS REPO PATH TARGET
demo-app https://kubernetes.default.svc default default OutOfSync Missing <none> <none> https://github.com/sarkartanmay393/Sample-GO-WebApp .
➜ argocd app get demo-app #Get demo-app info
Name: demo-app
Project: default
Server: https://kubernetes.default.svc
Namespace: default
URL: https://localhost:8085/applications/demo-app
Repo: https://github.com/sarkartanmay393/Sample-GO-WebApp
Target:
Path: .
SyncWindow: Sync Allowed
Sync Policy: <none>
Sync Status: OutOfSync from (2ee5cba)
Health Status: Missing
GROUP KIND NAMESPACE NAME STATUS HEALTH HOOK MESSAGE
Service default sample-service OutOfSync Missing
apps Deployment default sample-deployment OutOfSync Missing
4. Sync app in CLI
As this app is only created, the default sync status will be OutOfSync. To perform synchronization run the command -
➜ argocd app sync demo-app #Sync demo-app
TIMESTAMP GROUP KIND NAMESPACE NAME STATUS HEALTH HOOK MESSAGE
2022-08-18T14:13:47+05:30 apps Deployment default sample-deployment OutOfSync Missing
2022-08-18T14:13:47+05:30 Service default sample-service OutOfSync Missing
2022-08-18T14:13:48+05:30 Service default sample-service OutOfSync Missing service/sample-service created
2022-08-18T14:13:48+05:30 apps Deployment default sample-deployment OutOfSync Missing deployment.apps/sample-deployment created
2022-08-18T14:13:48+05:30 apps Deployment default sample-deployment Synced Progressing deployment.apps/sample-deployment created
2022-08-18T14:13:48+05:30 Service default sample-service Synced Healthy service/sample-service created
Name: demo-app
Project: default
Server: https://kubernetes.default.svc
Namespace: default
URL: https://localhost:8085/applications/demo-app
Repo: https://github.com/sarkartanmay393/Sample-GO-WebApp
Target:
Path: .
SyncWindow: Sync Allowed
Sync Policy: <none>
Sync Status: Synced to (2ee5cba)
Health Status: Progressing
Operation: Sync
Sync Revision: 2ee5cba61a4446ec05241edce5f781a7f4aa26de
Phase: Succeeded
Start: 2022-08-18 14:13:47 +0530 IST
Finished: 2022-08-18 14:13:48 +0530 IST
Duration: 1s
Message: successfully synced (all tasks run)
GROUP KIND NAMESPACE NAME STATUS HEALTH HOOK MESSAGE
Service default sample-service Synced Healthy service/sample-service created
apps Deployment default sample-deployment Synced Progressing deployment.apps/sample-deployment created
Now the deployed application is synced.
This will be the final view of our deployed application in the Argo CD User Interface.

- Access the Deployed App
Now check for services running under default namespace in kubernetes.
Run the command -
➜ kubectl get services #Get cluster services under default namespace.
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
kubernetes ClusterIP 10.96.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 40d
sample-service NodePort 10.96.22.35 <none> 8080:31000/TCP 17m
You need to port forward the sample-service to access the app.
Run the command -
kubectl port-forward svc/sample-service 8086:8080
Now, visit localhost:8086 to see.
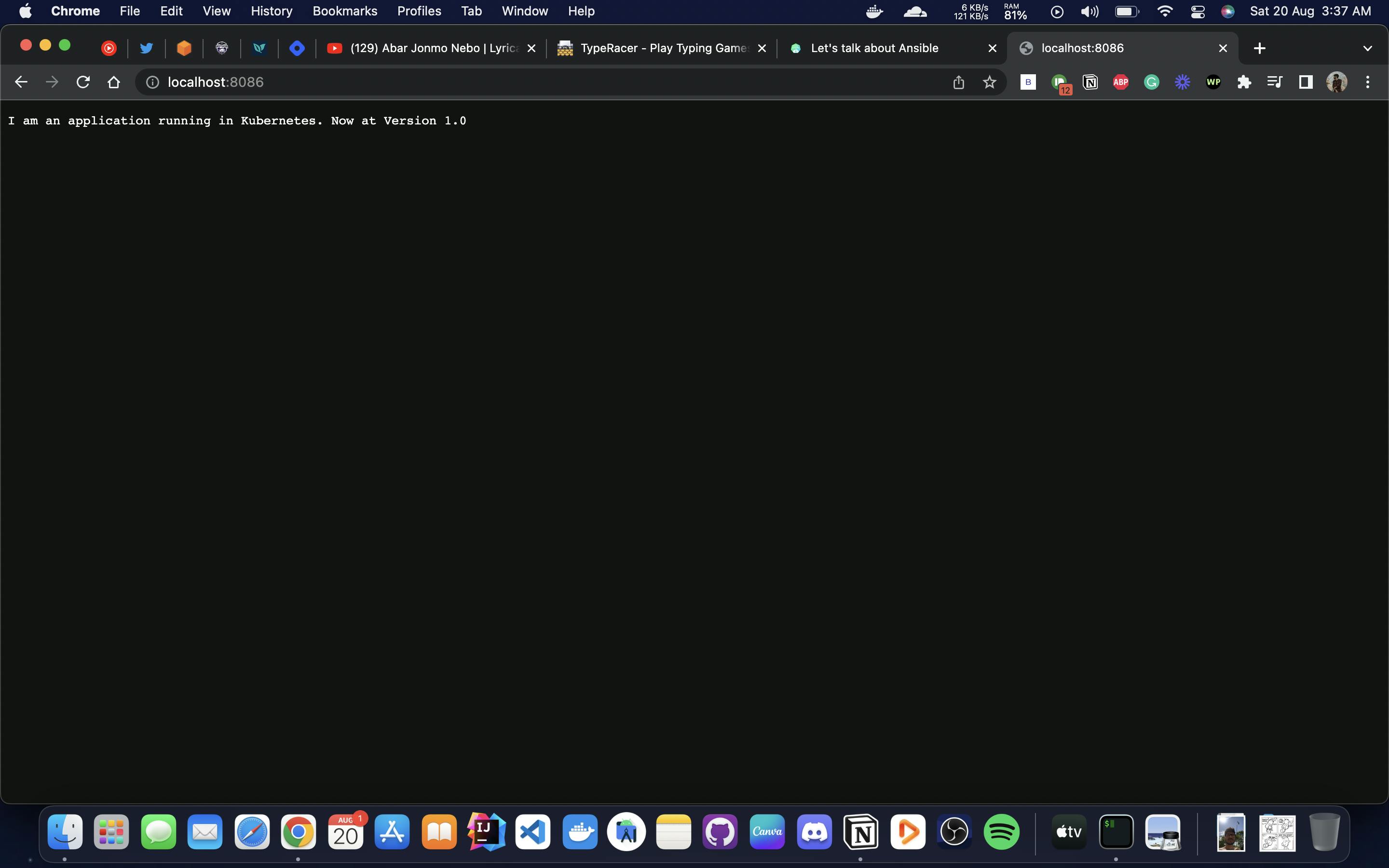
This is the Argo CD Beginners Article. Hope that you have learned something new. See you in my next article.
PS. Learning About Agro CD from Codefresh. For this article, I have taken references from Codefresh.
